If you’ve ever wondered how modern apps stay responsive while loading data, playing videos, or handling multiple users at once, the answer often lies in asynchronous programming.
At first, the term can sound intimidating. But once you understand the core idea, it becomes surprisingly simple — and incredibly powerful. Let’s break it down step by step, from the ground up.
Understanding the Core Idea
At its heart, asynchronous programming is a way of writing code that allows a program to start a task and move on to other work before that task finishes.
Instead of waiting around for slow operations to complete, the program stays productive.
Think of it like this:
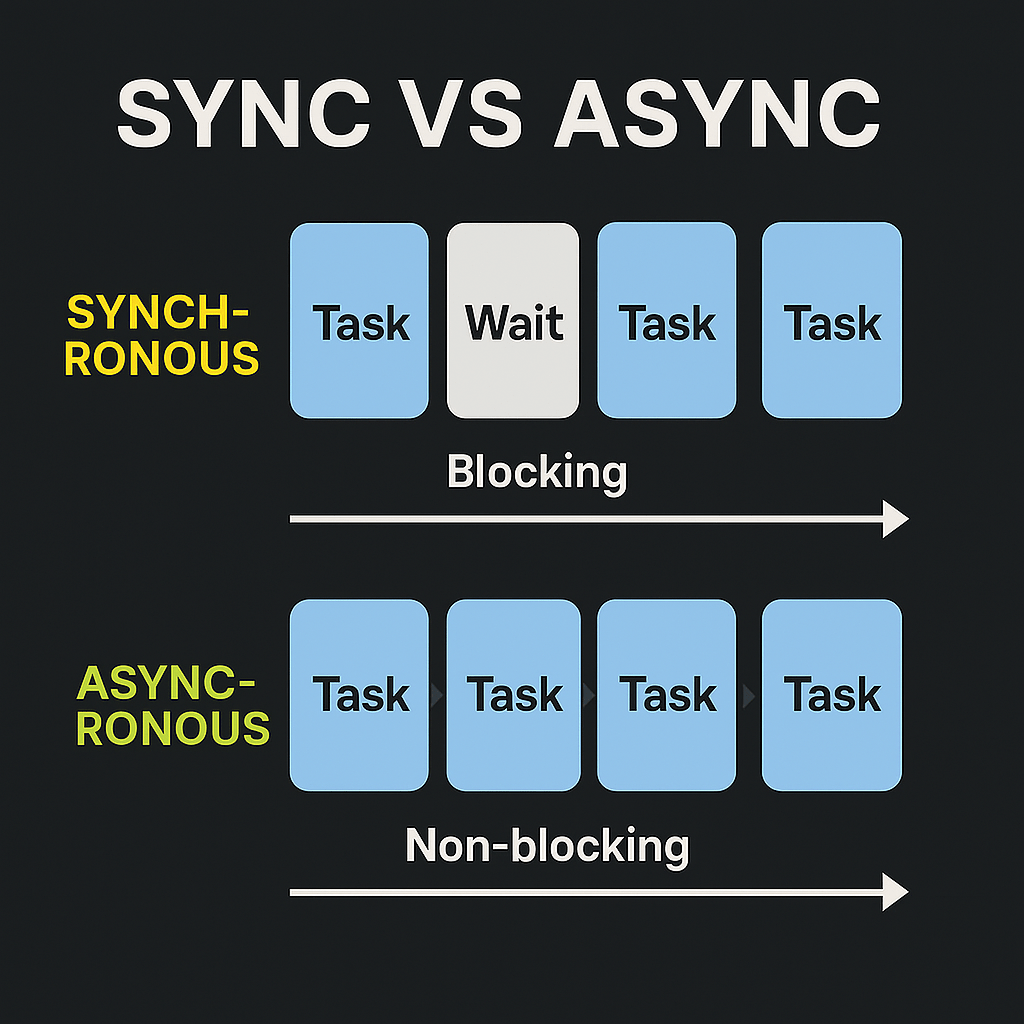
- Synchronous: Do one thing at a time, in order, waiting for each step to finish.
- Asynchronous: Start a task, set it aside, and continue doing other things while it runs in the background.
This difference may sound small, but it has a huge impact on performance and user experience.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous (With a Simple Example)
Synchronous Programming
Imagine you’re cooking and you put rice on the stove. While it’s cooking, you do nothing else. You just stand there waiting.
That’s synchronous behavior.
In code, it looks like this:
- Start task A
- Wait until task A finishes
- Start task B
- Wait again
If task A takes 5 seconds, everything else is frozen for 5 seconds.
Asynchronous Programming
Now imagine you put rice on the stove and start chopping vegetables while it cooks.
That’s asynchronous behavior.
In code:
- Start task A
- Move on to task B immediately
- Come back to task A when it’s done
This makes much better use of time and resources.
Why Asynchronous Programming Exists
Computers are incredibly fast, but some tasks are naturally slow, such as:
- Fetching data from the internet
- Reading or writing files
- Accessing a database
- Waiting for user input
- Sending emails or messages
If a program waits for each of these tasks to finish before doing anything else, it feels slow and unresponsive.
Asynchronous programming solves this by allowing programs to keep running smoothly while waiting on these slower operations.
Real-World Examples You Already Use
You encounter asynchronous programming every day, even if you don’t realize it.
Web Applications
- A website loads content while you scroll
- Notifications appear without refreshing the page
- Messages arrive while you’re typing
Mobile Apps
- Music plays while data syncs in the background
- Maps load directions while you’re moving
- Apps stay responsive during updates
Operating Systems
- Downloads continue while you work
- Multiple programs run at the same time
- System updates don’t freeze everything
All of this relies on asynchronous behavior behind the scenes.
How Asynchronous Programming Works (Conceptually)
While the technical details differ between languages, the conceptual flow is usually the same:
- Start a task that may take time
- Tell the system what to do when it finishes
- Continue running other code
- Handle the result later
This is often managed using ideas like:
- Callbacks
- Promises
- Futures
- Async/await syntax
You don’t need to master these immediately. What matters is understanding why they exist: to avoid waiting unnecessarily.
Key Benefits of Asynchronous Programming
1. Better Performance
Programs don’t sit idle while waiting for slow tasks.
2. Improved User Experience
Apps stay responsive instead of freezing or lagging.
3. Efficient Resource Usage
The system can handle more work with fewer resources.
4. Scalability
Servers can manage many users at once without blocking.
These advantages are why asynchronous programming is essential in modern software.
Common Misconceptions
“Asynchronous means faster”
Not always. It means smarter use of time, not instant execution.
“Asynchronous code runs in parallel”
Sometimes yes, sometimes no. Asynchronous code can still run on a single thread but switches tasks efficiently.
“It’s only for advanced developers”
While it can be complex at first, modern tools and syntax have made it much more beginner-friendly.
When You Should Use Asynchronous Programming
Asynchronous programming is ideal when your program:
- Waits on external systems
- Handles multiple users
- Performs background tasks
- Needs to stay responsive
If your program only does simple calculations, synchronous code may be perfectly fine.
Key Takeaways
- Asynchronous programming lets programs do multiple things without waiting
- It’s essential for modern apps, websites, and systems
- It improves responsiveness, performance, and scalability
- You already rely on it every day, even if you don’t see it
- Understanding the concept matters more than memorizing syntax
Once this idea clicks, many confusing programming concepts suddenly start to make sense.
If you enjoy learning how systems work and want to apply these ideas to business, productivity, and digital skills, you may also find value in my books on personal development, communication, and online income strategies available on Apple Books.
Leave a comment