If you’ve ever noticed a website URL starting with http:// or https:// and wondered what the difference is, you’re not alone. These two look almost the same, but they play very different roles when it comes to security, trust, and data protection.
In this guide, I’ll explain HTTP vs HTTPS in plain, beginner-friendly language—no technical background required.
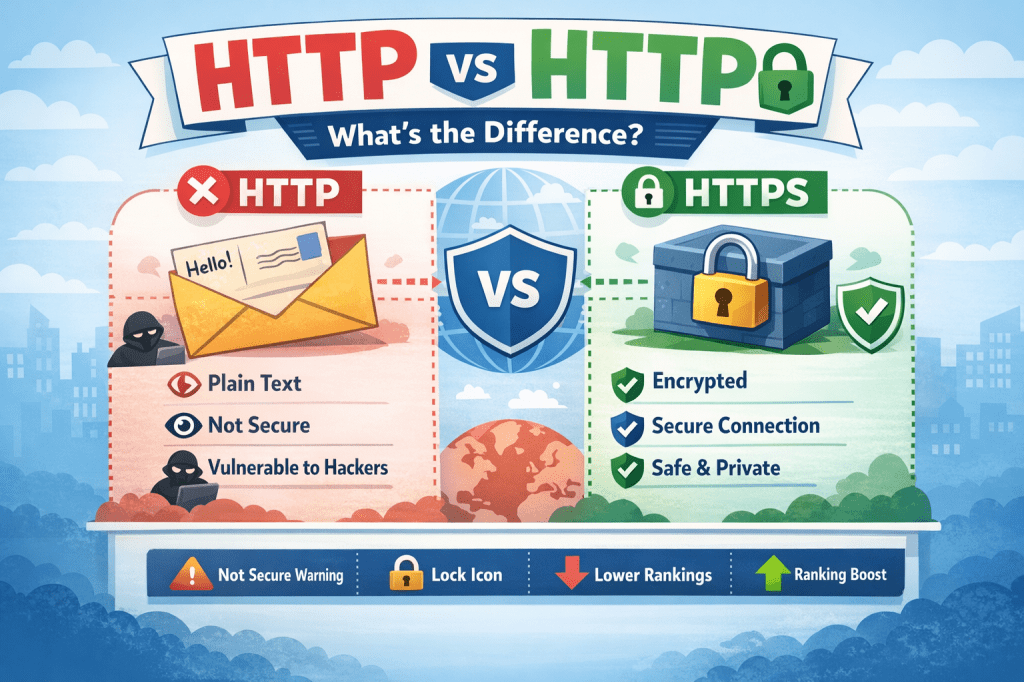
What Is HTTP?
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol.
It’s a set of rules that allows your browser (like Chrome or Safari) to communicate with a website’s server. Every time you open a webpage, submit a form, or click a link, HTTP helps move that information back and forth.
How HTTP Works (Simple Example)
Imagine sending a postcard through the mail:
- Anyone who handles it can read the message
- Anyone could change the message
- There’s no guarantee it reaches the right person unchanged
That’s essentially how HTTP works.
Key Characteristics of HTTP
- ❌ No encryption
- ❌ Data is visible to attackers
- ❌ Vulnerable to hacking and data theft
- ❌ Not safe for passwords or payments
In the early days of the internet, HTTP was fine because websites didn’t handle sensitive information. That’s no longer the case.
What Is HTTPS?
HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure.
It’s the secure version of HTTP and uses encryption to protect the data shared between your browser and the website.
How HTTPS Works (Simple Example)
Now imagine sending the same message in a locked box:
- Only the sender and receiver have the key
- No one else can read or change it
- You know it hasn’t been tampered with
That’s HTTPS.
What Makes HTTPS Secure?
HTTPS uses:
- SSL/TLS encryption
- Security certificates
- Identity verification
This ensures that:
- Data is encrypted
- The website is authentic
- Information stays private
Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
Here’s a clear side-by-side comparison:
1. Security
- HTTP: Data is sent as plain text
- HTTPS: Data is encrypted and protected
This is the most important difference.
2. Data Protection
- HTTP: Hackers can intercept usernames, passwords, and messages
- HTTPS: Even if intercepted, the data is unreadable
That’s why HTTPS is essential for:
- Logins
- Payments
- Contact forms
- Personal information
3. Trust and Credibility
Browsers clearly show the difference:
- HTTP → “Not Secure” warning
- HTTPS → Lock 🔒 icon
Users are far more likely to trust and stay on HTTPS websites.
4. SEO and Google Rankings
Google officially favors HTTPS websites.
- HTTPS sites get a ranking boost
- HTTP sites may lose traffic
- Chrome warns users before loading HTTP pages
If SEO matters to you at all, HTTPS is no longer optional.
5. Performance
Thanks to modern protocols like HTTP/2, HTTPS can actually be:
- Faster
- More efficient
- Better optimized for modern browsers
So security doesn’t come at the cost of speed anymore.
Why HTTPS Is Now the Standard
Today, HTTPS is used by:
- Online stores
- Blogs
- Business websites
- Social media platforms
- Even personal portfolios
In fact, most modern browsers discourage HTTP completely.
When Is HTTP Still Used?
Only in rare cases like:
- Local testing environments
- Internal networks
- Temporary development setups
For public websites, HTTP is outdated.
Is HTTPS Required for Small Websites?
Yes.
Even if your site:
- Doesn’t sell anything
- Doesn’t have logins
- Is “just a blog”
Visitors still expect security, and browsers enforce it.
HTTPS also:
- Protects user privacy
- Prevents data manipulation
- Builds long-term trust
How Websites Switch from HTTP to HTTPS
Behind the scenes, HTTPS requires:
- An SSL certificate
- Proper server configuration
- Redirects from HTTP to HTTPS
Most hosting providers now offer free SSL certificates, making the switch simple and affordable.
Key Takeaways
- HTTP is not secure
- HTTPS encrypts data and protects users
- Browsers and search engines prefer HTTPS
- Trust, SEO, and safety all depend on HTTPS
- Today, HTTPS is the default—not a bonus
If you’re building, managing, or even just choosing websites to trust, HTTPS should always be your standard.
If you’re interested in learning more about online business, digital skills, communication, and personal growth, you may find my books on Apple Books helpful as a next step.
Leave a comment