If you’ve ever opened Google Search Console and seen a warning like “Page indexing: Not found (404)”, it can feel alarming—especially when you notice dozens of affected URLs. Many site owners immediately worry that their rankings or traffic are in danger.
The good news?
404 errors are common, often misunderstood, and usually fixable once you know what’s actually happening.
This article breaks down what Google Search Console 404 errors mean, why they appear, and how to fix them the right way—step by step, in plain language.
What Does “Not Found (404)” Mean in Google Search Console?
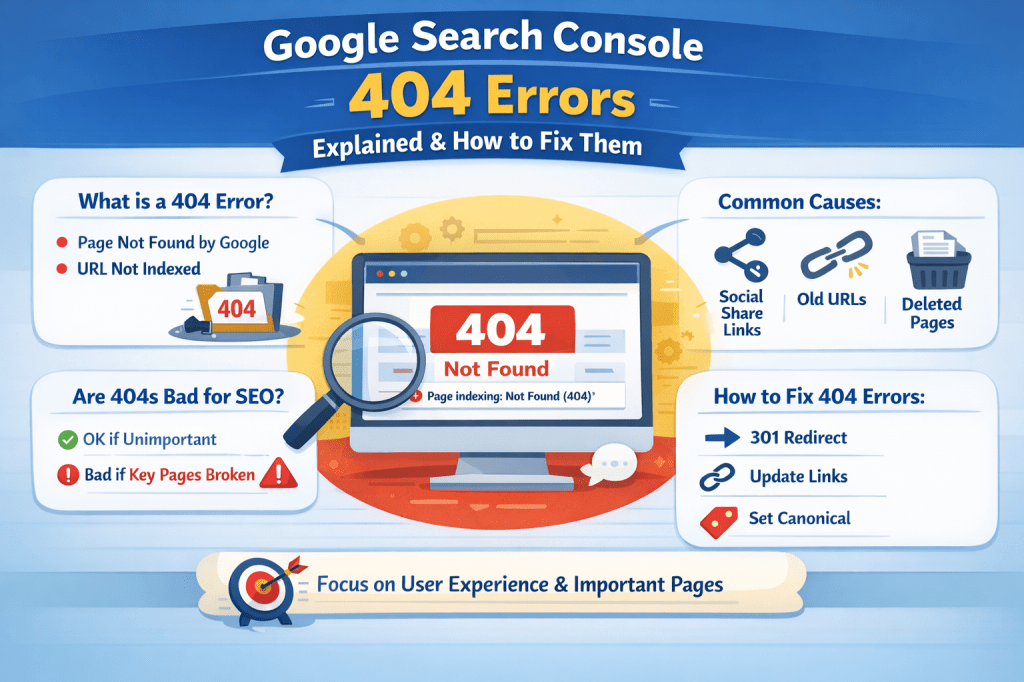
A 404 error means that Google tried to access a specific URL on your website, but the page was not found.
In simple terms:
- Google asked for a page
- Your site replied: “That page doesn’t exist”
When this happens, Google marks the URL as Not indexed, which means:
- The page will not appear in Google search results
- It won’t bring any organic traffic
Importantly, 404 errors are not penalties. They are signals.
Why Google Is Crawling Pages That Don’t Exist
Looking at the URLs in your report, many of them include parameters like:
?share=twitter?share=x?nb=1
This gives us a strong clue about the root cause.
Common Reasons These 404 Errors Appear
1. Social Media Share URLs
When someone shares your article on Twitter (X), WhatsApp, or another platform, extra tracking parameters get added to the URL.
Example:
/what-is-seo-a-beginners-guide/?share=twitterIf your website isn’t set up to handle these parameters, it may return a 404 error, even though the main article exists.
2. URL Structure Changes
If you:
- Changed your permalink structure
- Updated post slugs
- Deleted or renamed articles
Google may still try to crawl the old URLs it previously discovered.
3. Deleted or Unpublished Content
Pages that were:
- Removed intentionally
- Drafted but later deleted
- Published briefly and then removed
can still remain in Google’s crawl history for a while.
4. Internal or External Broken Links
Sometimes:
- Your own site links to a non-existent URL
- Another website links incorrectly to your content
Google follows those links and hits a dead end.
Are 404 Errors Bad for SEO?
This is where many people panic unnecessarily.
The Truth:
- A few 404 errors are normal
- Google expects them
- They do not harm your site by default
However, they can become a problem if:
- Important pages return 404
- Many internal links point to 404 pages
- High-value backlinks lead to 404 URLs
In short:
404s are only an SEO issue when they affect real users or important pages.
How to Decide Which 404 Errors Need Fixing
Before clicking “Validate Fix,” you should evaluate each URL logically.
Ask yourself:
- Does this page still exist (without parameters)?
- Was this page important for traffic or SEO?
- Is it being linked internally or externally?
Based on the answers, you choose the correct solution.
The Right Way to Fix Google Search Console 404 Errors
Option 1: Do Nothing (Yes, Sometimes This Is Correct)
If:
- The page was intentionally deleted
- The URL was never meant to exist
- It only has tracking parameters
Then:
- Leave it as 404
- Google will eventually drop it from reports
This is perfectly acceptable.
Option 2: Use a 301 Redirect (Best for Renamed Pages)
If the content still exists under a new URL, set up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one.
Example:
Old URL → New URLThis:
- Preserves SEO value
- Sends users to the right page
- Signals Google to update its index
Option 3: Canonicalize Parameter URLs
If your CMS allows it, make sure:
- URLs with
?share=parameters point to the main canonical URL - Google understands they are the same page
This prevents duplicate crawling and unnecessary 404 reports.
Option 4: Fix Internal Links
Check:
- Menus
- Blog posts
- Footer links
Make sure none of them point to URLs that no longer exist.
When Should You Click “Validate Fix” in Search Console?
Only click Validate Fix when:
- You’ve added redirects
- Fixed broken internal links
- Corrected technical issues
If the pages are intentionally gone, you don’t need to validate. Google will clean them up over time.
Key Takeaways
- A 404 error means Google couldn’t find a page, not that your site is broken
- URLs with share parameters often cause false alarms
- Not all 404 errors need fixing
- Redirect important pages, ignore irrelevant ones
- Focus on user experience, not chasing a “perfect” report
When handled calmly and strategically, 404 errors are simply part of maintaining a healthy website—not something to fear.
If you’re interested in learning more about SEO, online business, digital skills, and personal growth, you may also find value in my books available on Apple Books, where I break down complex topics into clear, practical lessons for beginners.
Leave a comment