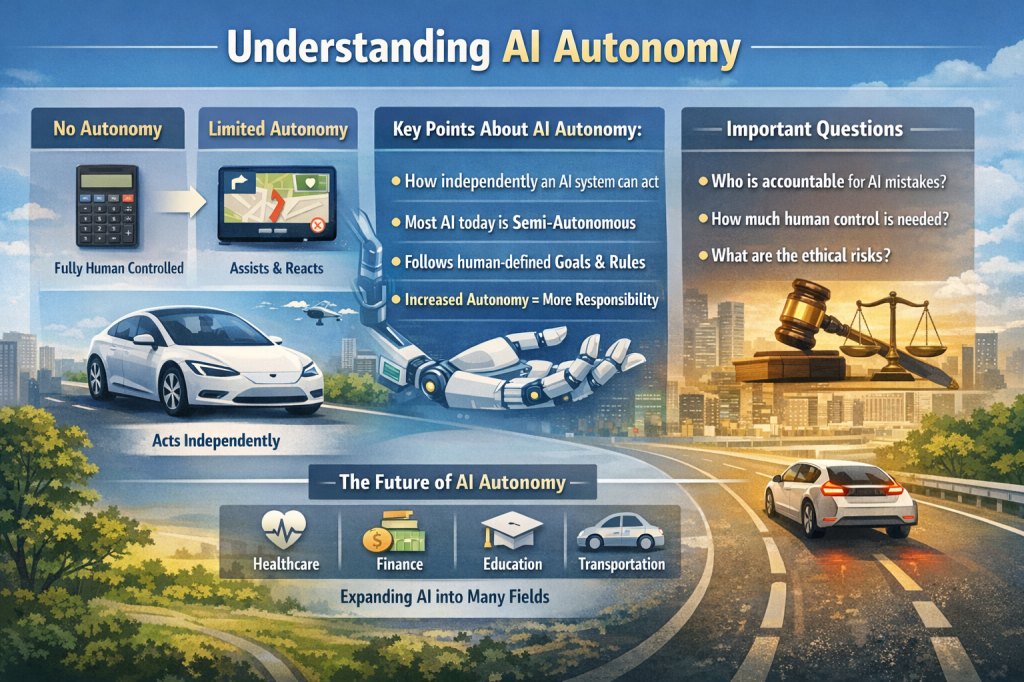
AI autonomy simply means how much freedom an artificial intelligence system has to make decisions and take actions on its own, without needing constant human input. In easy terms, the more autonomous an AI is, the less it needs a human to tell it what to do at every step.
Think of a basic calculator. It only works when you press buttons—that’s zero autonomy. Now think of a navigation app that automatically reroutes you when there’s traffic. That app is showing limited autonomy because it reacts on its own using data. At the highest levels, AI autonomy looks more like self-driving cars or smart agents that plan tasks, learn from results, and act independently toward a goal.
AI autonomy usually grows in stages. First, humans fully control the system. Next, AI assists humans by suggesting options. Then it can act on its own but under human supervision. Finally, in advanced cases, AI can operate independently within defined boundaries. Most AI systems today sit somewhere in the middle—not fully autonomous, but not fully dependent either.
A common real-world example is self-driving technology. Companies like Tesla use AI that can steer, brake, and adjust speed on its own, but still require human oversight. Another example is AI chat systems such as those developed by OpenAI, which can generate responses independently but follow strict rules and limits.
One important thing to understand is that AI autonomy does not mean consciousness or free will. Autonomous AI doesn’t “want” anything. It follows goals, rules, and data patterns set by humans. The autonomy is about execution, not intention.
As AI autonomy increases, so do important questions around safety, ethics, and responsibility. Who is accountable if an autonomous AI makes a mistake? How much control should humans keep? These questions are shaping laws and policies around the world.
Key Takeaways
- AI autonomy means how independently an AI system can act
- Most AI today is semi-autonomous, not fully independent
- Autonomous AI follows human-defined goals, not emotions or desires
- Higher autonomy increases efficiency but also responsibility
Looking Forward
In the future, AI autonomy will likely expand in areas like healthcare, finance, education, and transportation. We’ll see AI systems that manage schedules, monitor risks, and optimize decisions in real time—while humans focus more on creativity, strategy, and ethics. The key will be finding the right balance between automation and human control.
If you enjoy simple explanations of complex AI topics, explore my books on Shafaat Ali, Apple Books, where I break down technology, AI, and the future in a clear, practical way.
Leave a comment