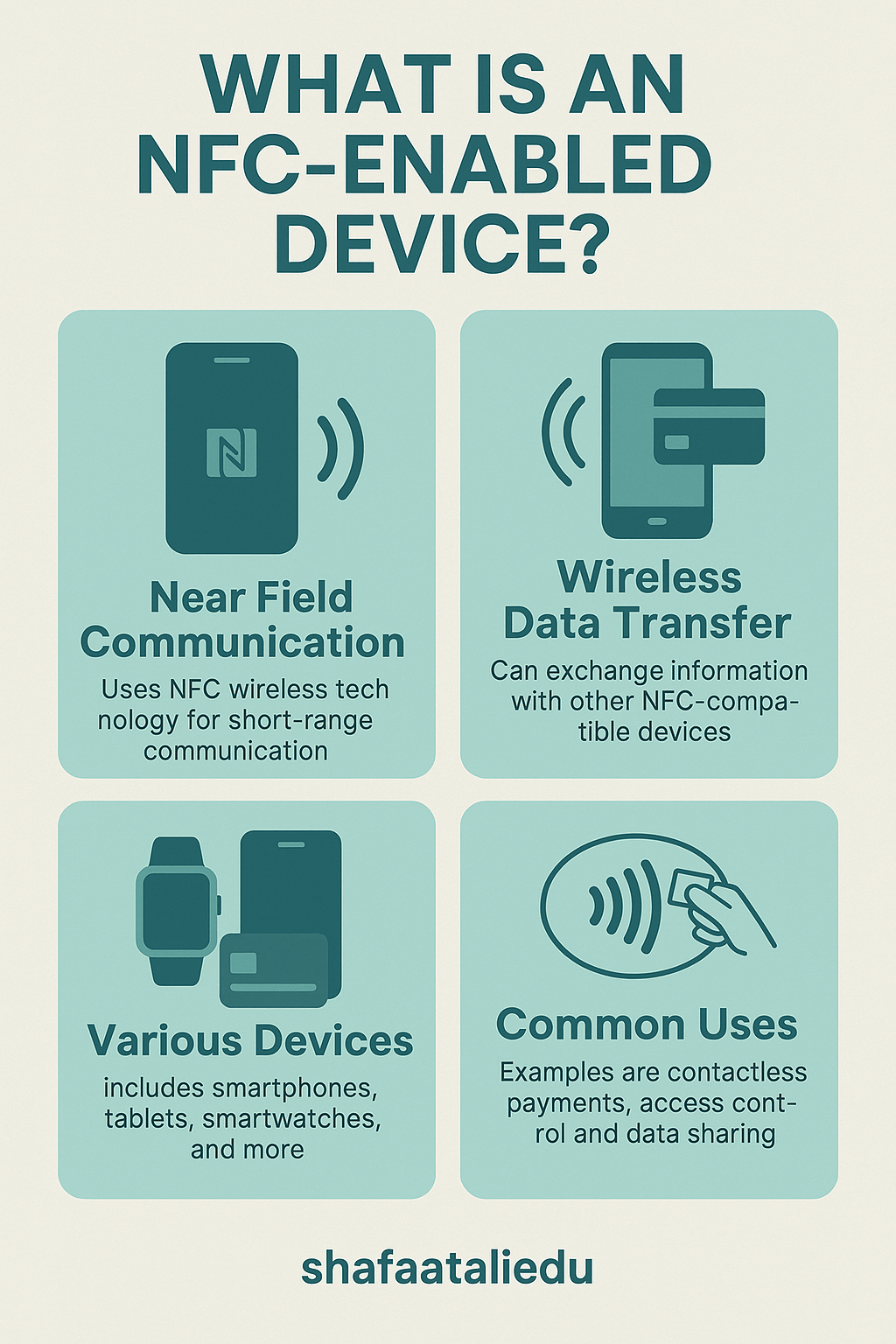
An NFC-enabled device is any gadget that has built-in Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. This allows it to wirelessly exchange data with other NFC devices or tags when they’re just a few centimeters apart—usually less than 4 cm. If you’ve ever tapped your phone to pay at a store or scanned a metro card, chances are you were using an NFC-enabled device.
The most common NFC-enabled devices include smartphones, smartwatches, tablets, contactless credit/debit cards, wireless earbuds, and even some modern laptops. For example, if your phone supports Google Pay, Apple Pay, or Samsung Pay, then it’s NFC-enabled.
Here’s a simple way to think about it: imagine your phone has a tiny walkie-talkie that only works when it’s extremely close to another walkie-talkie. That’s how NFC works—it’s like a private conversation between devices right next to each other.
Everyday uses of NFC-enabled devices:
- Mobile payments: Tap your phone or watch at a checkout terminal.
- Transit access: Use your phone instead of a metro card.
- Smart posters: Tap your phone on an ad to get more info or open a website.
- File sharing: Send photos or contacts between phones (on Android).
- Pairing gadgets: Quickly connect your phone to Bluetooth speakers or earbuds.
To check if your device is NFC-enabled, go to its settings and search for “NFC.” If it shows up, you’ve got it.
NFC is all about convenience and speed—with security built-in. And as more devices and places adopt it, your NFC-enabled gadgets will become even more useful.
The future? Your phone could become your wallet, key, ID, and more—all thanks to NFC.
Leave a reply to What is NFC (Near Field Communication)? – Shafaat Ali Education Cancel reply