Have you ever felt mentally exhausted after reading too much information, watching long videos, or trying to learn something new very quickly? If yes, you have experienced cognitive overload.
Cognitive overload is a common problem in today’s fast-paced, information-heavy world. Let’s break it down in simple terms so you can clearly understand what it is, why it happens, and how to deal with it.
What Is Cognitive Overload?
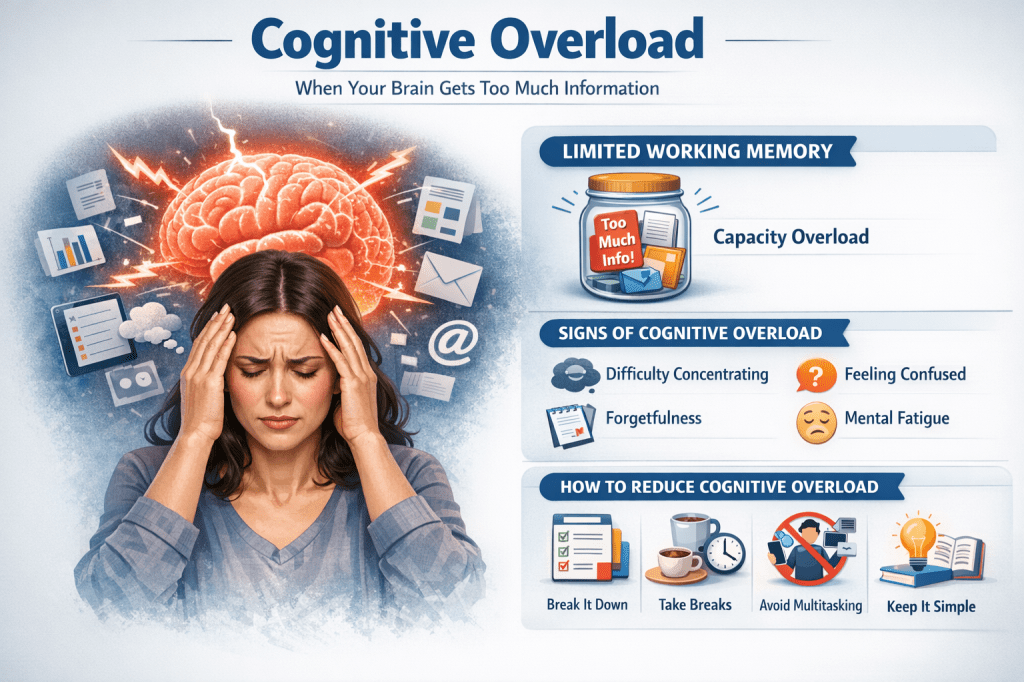
Cognitive overload happens when your brain receives more information than it can process at one time.
Our brains have a limited capacity to think, understand, and remember things. When too much information is presented at once, the brain gets overwhelmed. As a result, learning becomes harder, decision-making slows down, and mistakes increase.
In simple words:
- Your brain feels “full”
- You struggle to focus
- You feel stressed or mentally tired
How the Brain Processes Information
To understand cognitive overload, it helps to know how the brain works.
The brain uses working memory to temporarily hold and process information. This memory is very limited.
For example:
- You can easily remember 3–5 items
- But remembering 15 items at once is difficult
When too much information enters working memory at the same time, the brain cannot handle it properly. That’s when cognitive overload occurs.
Common Causes of Cognitive Overload
Cognitive overload doesn’t happen randomly. It usually comes from specific situations.
1. Too Much Information at Once
Reading long articles, watching lengthy lectures, or studying many topics together can overload the brain.
2. Multitasking
Trying to do many things at the same time, such as:
- Studying while checking your phone
- Working while watching videos
This divides attention and increases mental pressure.
3. Complex or Unclear Information
Information that is:
- Poorly explained
- Full of jargon
- Disorganized
…makes the brain work harder than necessary.
4. Stress and Fatigue
When you are tired or stressed, your brain’s ability to process information decreases, making overload more likely.
Signs and Symptoms of Cognitive Overload
You may be experiencing cognitive overload if you notice these signs:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Forgetting things quickly
- Feeling confused or mentally “foggy”
- Slower decision-making
- Frustration or irritability
- Mental exhaustion
These signs are your brain’s way of telling you it needs a break.
Real-Life Examples of Cognitive Overload
Here are some simple examples to make it clearer:
- Students: Studying multiple subjects for hours without breaks
- Office workers: Attending back-to-back meetings with no time to process information
- Social media users: Scrolling endlessly through news, posts, and videos
- Online learners: Watching long courses without summaries or pauses
In all these cases, the brain receives more input than it can handle.
Why Cognitive Overload Is a Problem
Cognitive overload affects both learning and performance.
Negative Effects Include:
- Poor understanding of information
- Low productivity
- Increased errors
- Reduced creativity
- Higher stress levels
Instead of learning faster, you actually learn less when your brain is overloaded.
How to Reduce Cognitive Overload
The good news is that cognitive overload can be managed easily with small changes.
1. Break Information into Small Parts
Instead of learning everything at once:
- Learn one concept at a time
- Use short study sessions
2. Take Regular Breaks
Short breaks help the brain reset and process information better.
3. Avoid Multitasking
Focus on one task at a time. Single-tasking improves understanding and memory.
4. Use Simple Language and Visuals
Clear explanations, bullet points, and images reduce mental effort.
5. Organize Information
Use:
- Headings
- Lists
- Summaries
This makes content easier to digest.
Cognitive Overload in Learning and Education
Teachers, trainers, and content creators should be careful not to overload learners.
Good learning design includes:
- Clear structure
- Step-by-step explanations
- Examples and visuals
- Short lessons instead of long ones
This approach helps learners understand and remember better.
Key Takeaways
- Cognitive overload happens when the brain gets too much information at once
- The brain has limited working memory
- Multitasking and complex information increase overload
- Overload reduces learning, focus, and productivity
- Simple strategies can reduce mental stress and improve understanding
Looking Ahead
As information continues to grow in our digital world, understanding cognitive overload becomes more important than ever. By learning how your brain works and respecting its limits, you can study smarter, work better, and feel less stressed.
Small changes in how you learn and consume information can make a big difference.
Leave a comment